728x90
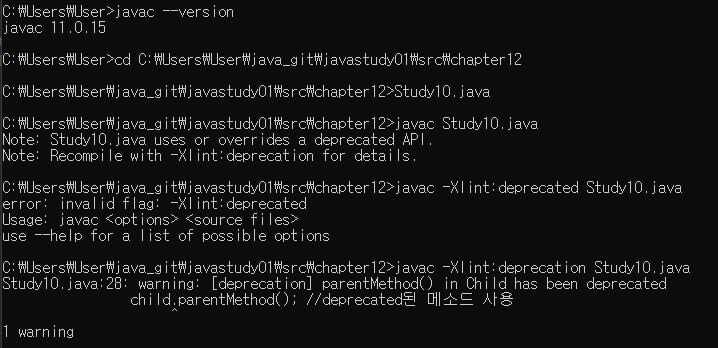
※cmd에서 javac 명령어 사용
문제 : javac --version은 정상적으로 실행되나 class 파일로 컴파일이 안됨.
해결 :
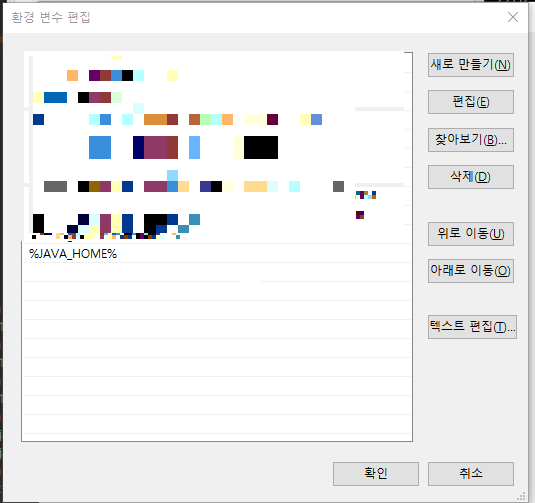
- 설정 - 정보 - 고급 시스템 설정 - 환경 변수
- 시스템 변수에 변수와 값이 설정되어 있는지 확인 -> 없으면(3번 항목으로), 있으면(4번 항목으로)
- 시스템 변수 - 새로 만들기(W)
변수 이름 : JAVA_HOME
변수 값 : jdk가 설치된 경로 \bin 파일로 설정 ex)C:\Program Files\ojdkbuild\java-11-openjdk-11.0.15-1\bin - 시스템 변수 - 변수 Path - 편집(I)
환경 변수 편집 - 새로 만들기 %JAVA_HOME%

와일드카드 <?>
- 하나의 참조 변수로 대입된 타입이 다른 객체를 참조 가능
ArrayList<? extends Product> list = new ArrayList<Tv>(); //불일치하지만 가능
ArrayList<? extends Product> list = new ArrayList<Audio>();
- <? super T> : 와일드 카드 하한 제한. T와 그 조상만 가능
- <? extends T> : 와일드 상한 제한. T와 그 자손만 가능
- <?> : 제한 없음. 모든 타입이 가능 == <? extends Object>와 동일
- 메소드의 매개 변수에 와일드 카드를 사용
package chapter12;
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Fruit2 {public String toString() {return "Fruit";}}
class Apple2 extends Fruit2{public String toString() {return "Apple";}}
class Grape2 extends Fruit2{public String toString() {return "Grape";}}
class Juice{
String name;
Juice(String name){this.name = name+"Juice";}
public String toString() {return name;}
}
class Juicer{
static Juice makeJuice(FruitBox2<? extends Fruit2> box) {
String tmp = "";
for(Fruit2 f : box.getList())
tmp += f + " ";
return new Juice(tmp);
}
}
class FruitBox2<T extends Fruit2> extends Box2<T>{}
class Box2<T>{
ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<T>();
void add(T item) { list.add(item);}
T get(int i) { return list.get(i);}
ArrayList<T> getList() {return list;}
int size() { return list.size();}
public String toString() {return list.toString();}
}
public class Study06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FruitBox2<Fruit2> fruitBox = new FruitBox2<Fruit2>();
FruitBox2<Apple2> appleBox = new FruitBox2<Apple2>(); //가능
// FruitBox2<Fruit2> appleBox = new FruitBox2<Apple2>(); //에러
// FruitBox2<? extends Fruit2> appleBox = new FruitBox2<Apple2>();
//Fruit2와 그 자손
fruitBox.add(new Apple2());
fruitBox.add(new Grape2());
appleBox.add(new Apple2());
appleBox.add(new Apple2());
System.out.println(Juicer.makeJuice(fruitBox));
System.out.println(Juicer.makeJuice(appleBox));
}
}
제네릭 메소드
- 제네릭 타입이 선언된 메소드(타입 변수는 메소드 내에서만 유효)
static <T> void sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c)- 클래스의 타입 매개변수<T>와 메소드의 타입 매개변수 <T>는 별개
class FruitBox<T>{ //제네릭 클래스
...
//제네릭 메소드
//제네릭 클래스 <T>와 제네릭 메소드 <T> 타입 문자 일치하지만 다른 타입 변수임
static <T> void sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c){
...
}
}- 메소드를 호출할 때마다 타입을 대입해야함(대부분 생략 가능)
FruitBox<Fruit> fruitBox = new FruitBox<Fruit>();
FruitBox<Apple> appleBox = new FruitBox<Apple>();
...
System.out.println(Juicer.<Fruit>makeJuice(fruitBox));
System.out.println(Juicer.<Apple>makeJuice(appleBox));
static<T extends Fruit> Juice makeJuice(FruitBox<T> box){ //와일드 카드는 하나의 참조변수로 서로 다른 타입이 대인된 여러 제네릭 객체를 다루기 위한 것
String tmp = "";
for(Fruit f : box.getList()) tmp += f + "";
return new Juice(tmp);
}- 메소드를 호출할 때 타입을 생략하지 않을 때는 클래스 이름 생략 불가
System.out.println(<Fruit>makeJuice(fruitBox)); //에러. 클래스 이름 생략 불가
System.out.println(this.<Fruit>makeJuice(fruitBox));
System.out.println(Juicer.<Fruit>makeJuice(fruitBox));
제네릭 타입의 형 변환
- 제네릭 타입과 원시 타입 간의 형 변환은 바람직하지 않음.(경고 발생)
Box<Object> objBox = null;
Box box = (Box)objBox; //제네릭 타입 → 원시 타입. 가능은 하지만, 경고(노란색 전구) 발생
objBox = (Box<Object>)box; //원시 타입 → 제네릭 타입. 가능은 하지만, 경고(노란색 전구) 발생
//=======================================
Box<Object> objBox = null;
Box<String> strBox = null;
objBox = (Box<Object>)strBox; // 에러. Box<String> → Box<Object>
strBox = (Box<String>)objBox; // 에러. Box<Object> → Box<String>- 와일드 카드가 사용된 제네릭 타입으로는 형 변환 가능
Box<Object> objBox = (Box<Object>)new Box<String>(); //에러. 형 변환 불가능
Box<? extends Object> wBox = (Box<? extends Object>)new Box<String>(); //가능
// == Box<? extends Object> wBox = new Box<String>();
//매개변수 FruitBox<Fruit>, FruitBox<Apple>, FruitBox<Grape> 등이 가능
static Juice makeJuice(FruitBox<? extends Fruit> box){...}
FruitBox<? extends Fruit> box = new Fruit<Fruit>(); //가능
FruitBox<? extends Fruit> box = new Fruit<Apple>(); //가능
package chapter12;
import java.util.ArrayList;
interface Eatable{}
class Fruit implements Eatable{
public String toString() {return "Fruit";}
}
class Apple extends Fruit{public String toString() {return"Apple";}}
class Grape extends Fruit{public String toString() {return"Grape";}}
class Toy {public String toString() {return"Toy";}}
public class Study07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Box b = null; //Box b = new Box<String>();
// Box<String> bStr = null;
// b = (Box)bStr; //Box<String> → Box 가능. 경고
// bStr = (Box<String>)b; //Box → Box<String> 가능. 경고
// FruitBox<Fruit> fruitbox = new FruitBox<Fruit>();
FruitBox<? extends Fruit> fruitbox = (FruitBox<? extends Fruit>)new FruitBox<Fruit>(); //타입 불일치로 (FruitBox<? extends Fruit>)들어가야하지만 생략
FruitBox<Apple> applebox = new FruitBox<Apple>(); //가능
// FruitBox<? extends Fruit> applebox = new FruitBox<Apple>(); //가능
FruitBox<Apple> appleBox1 = (FruitBox<Apple>)applebox; //가능. 경고발생
FruitBox<Fruit> fruitBox = new FruitBox<Fruit>();
FruitBox<Apple> appleBox = new FruitBox<Apple>();
FruitBox<Grape> grapeBox = new FruitBox<Grape>();
// FruitBox<Grape> grapeBox = new FruitBox<Apple>(); // 에러. 타입 불일치
// FruitBox<Toy> toyBox = new FruitBox<Toy>(); // 에러.
fruitBox.add(new Fruit());
fruitBox.add(new Apple());
fruitBox.add(new Grape());
appleBox.add(new Apple());
// appleBox.add(new Grape()); // 에러. Grape는 Apple의 자손이 아님
grapeBox.add(new Grape());
System.out.println("fruitBox-"+fruitBox);
System.out.println("appleBox-"+appleBox);
System.out.println("grapeBox-"+grapeBox);
}
}
class FruitBox<T extends Fruit & Eatable> extends Box<T> {}
class Box<T> {
ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<T>();
void add(T item) { list.add(item); }
T get(int i) { return list.get(i); }
int size() { return list.size(); }
public String toString() { return list.toString();}
}
제네릭 타입의 제거
컴파일러는 제네릭 타입을 제거하고, 필요한 곳에 형 변환 함
//1. 제네릭 타입의 경계(bound)를 제거
class Box<T extends Fruit>{
void add(T t){
...
}
}
// 컴파일 후 코드
class Box{
void add(Fruit t){
...
}
}
//2. 제네릭 타입 제거 후 타입이 불일치하면, 형 변환을 추가
T get(int i){
return list.get(i);
}
// →
Fruit get(int i){
return (Fruit)list.get(i);
}
//3. 와일드 카드가 포함된 경우, 적절한 타입으로 형 변환 추가
static Juice makeJuice(FruitBox<? extends Fruit>box){
String tmp = "";
tmp += f + " ";
return new Juice(tmp);
}
// →
static Juice makeJuice(FruitBox box){
String tmp = "";
Iterator it = box.getList().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
tmp += (Fruit)it.next() + " ";
}
return new Juice(tmp);
}
728x90