데이터 조작어
데이터 수정 : UPDATE
SQL> UPDATE 테이블명
SET 컬럼명 = 값
[WHERE 조건]
테이블의 특정 행(데이터)을 수정하는 명령어
예제1)
113번 사원의 부서 확인 → 부서 100
select employee_id, last_name, department_id
from employees
where employee_id = 113;
113번의 사원의 부서를 50으로 바꾸기
update employees
set department_id = 50
where employee_id = 113;
select employee_id, department_id, last_name
from employees
where employee_id=113;

where 절 작성 시 특정행이 수정된 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
만약 where 절 없이 update구문을 사용한다면 컬럼값 전체가 바뀜
예제2)
select employee_id, last_name, salary
from copy_emp;
copy_emp 테이블에서 전 직원의 salary를 10% 인상하기
update copy_emp
set salary = 1.1*salary;

앞에 언급했듯이 update구문에서 where절이 생략하면 모든 값이 변경됨.
또한 update에도 서브쿼리를 사용할 수 있음
예제3)
copy_emp 테이블에 employee_id가 113번인 사원의 job_id와 salary를
employees테이블의 employee_id가 205인 사원과 같게 만들고 출력
먼저, 각각의 정보가 얼마인지 확인(변경하기 전을 확인해둬야 변경이 되었는지 알 수 있기 때문)
select *
from employees
where employee_id = 113;
job_id : FI_ACCOUNT, salary : 6900
select *
from employees
where employee_id=205;
job_id : AC_MGR , salary : 12000
변경
update copy_emp
set job_id = (select job_id from employees where employee_id = 205),
salary = (select salary from employees where employee_id = 205)
where employee_id = 113;
변경 결과 확인
select * from copy_emp where employee_id = 113;

set절에 서브쿼리가 들어간 예제이다.
다음으로는 where절에 서브쿼리가 들어간 update구문을 해보자
예제4)
select department_id from departments where location_id = 1800;
department_id : 20
update copy_emp
set salary = 1.1 * salary
where department_id = (select department_id from departments where location_id = 1800);
확인
select employee_id, last_name, salary, department_id
from copy_emp
where department_id = (select department_id from departments where location_id = 1800);

데이터 삭제 : DELETE
SQL> DELETE [FROM] 테이블명
[WHERE 조건]
테이블의 특정 행을 삭제하는 명령어
where절 없이 delete구문을 작성하면 모든 행을 삭제 됨.
예제1
department 테이블로부터 department_id가 320 삭제
select * from departments order by department_id desc;

delete from departments where department_id = 320;
확인
select * from departments order by department_id desc;

예제 2
copy_emp 테이블로부터 모든 행 삭제
delete from copy_emp;
확인
select * from copy_emp;

※employees 테이블을 사용해서 copy_emp 테이블로 데이터 복사
insert into copy_emp
select *
from employees;
확인
select * from copy_emp;
예제 3
select department_id from departments where location_id = 1800;
department_id : 20
delete from copy_emp
where department_id = (select department_id from departments where location_id = 1800);
확인
select *
from copy_emp
where department_id = (select department_id from departments where location_id = 1800);

트랜잭션 제어어(TCL)
하나의 논리적인 작업단위로 여러 개의 DML이 모여 하나의 트랜잭션이 구성되는데
트랜잭션 제어 명령어에는 commit(작업저장), rollback(작업취소), savepoint(트랜잭션 진행 중 되돌아갈 지점)가 있음
MySQL workbench에서 트랜잭션 설정
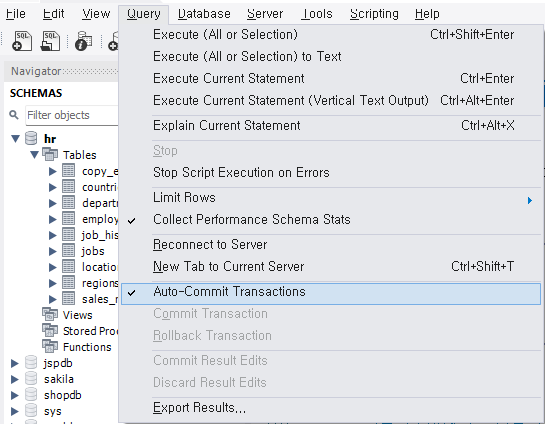
Query - Auto-Commit Transactions 활성화
DML 실행 시 바로 저장됨. 별도로 commit을 해주지 않아 편하지만, 작업 실수 시 되돌릴 수 없음
Query - Auto-Commit Transcations 비활성화(그림 10 Auto-Commit Transaction 체크 해제)
작업 실수 시 되돌릴 수 있으나, 수동으로 commit, rollback 가능하여 DML 실행 후 commit, rollback을 결정해야함.
변경 작업을 영구히 저장하는 명령어
SQL>commit;
변경 작업을 트랜잭션 처음으로 되돌리는 명령어
SQL> rollback;
트랜잭션 진행 중 되돌아갈 지점을 생성하는 명령어
ex)
insert ~~~;
update ~~~;
insert ~~~;
savepoint 포인트명;
delete ~~~~;
update ~~;
rollback to 포인트명;
Auto-Commit 비활성화 한 후 작업
-- 트랜잭션 시작
update copy_emp
set salary = 29000
where employee_id = 100;
update copy_emp
set salary = 27000
where employee_id = 102;
update copy_emp
set department_id = 50
where employee_id = 107;
select * from copy_emp where employee_id in (100,102,107); -- 미리보기, 저장되지 않고 임시 데이터 상태임.
commit; --저장 → 트랜잭션 종료
-- 트랜잭션 시작
delete from copy_emp;
select * from copy_emp;
rollback; -- 작업 취소, 트랜잭션 종료
select * from copy_emp;
update copy_emp
set department_id = 80
where employee_id = 100;
select * from copy_emp where employee_id = 100;
update copy_emp
set salary = salary * 1.2
where employee_id = 200;
select * from copy_emp where employee_id in (100,200);
savepoint savepoint1; -- 돌아올수있는 저장점 생성
update copy_emp
set salary = salary + 5000
where employee_id = 205;
select * from copy_emp where employee_id = 205;
rollback to savepoint1; -- savepoint1 저장점으로 되돌리기
select * from copy_emp where employee_id = 205;
commit; -- 작업 저장 → 트랜잭션 종료
-- 연습문제 1
create table my_employee
(id int primary key auto_increment,
last_name varchar(25),
first_name varchar(25),
userid varchar(8),
salary int);
-- 연습문제 2
desc my_employee;
-- 연습문제 3
insert into my_employee(last_name, first_name, userid, salary)
values ('Patel', 'Ralph', 'rpate1', 895),
('Dancs', 'Betty', 'bdancs', 860),
('Biri', 'Ben', 'bbiri', 1100),
('Newman', 'Chad', 'cnewman', 750);
-- 연습문제 4
select * from my_employee;
-- 연습문제 5
commit;
-- 연습문제 6
update my_employee set last_name = 'Drexler' where id = 3;
-- 연습문제 7
update my_employee set salary = 1000 where salary < 900;
-- 연습문제 8
select * from my_employee;
-- 연습문제 9
delete from my_employee where id = 2;
-- 연습문제 10
select * from my_employee;
-- 연습문제 11
commit;
-- 연습문제 12
insert into my_employee(last_name, first_name, userid, salary)
values('Ropeburn','Audrey','aropebur',1550);
-- 연습문제 13
select * from my_employee;
-- 연습문제 14
savepoint save1;
-- 연습문제 15
delete from my_employee;
-- 연습문제 16
select * from my_employee;
-- 연습문제 17
rollback to save1;
-- 연습문제 18
select * from my_employee;
-- 연습문제 19
commit;
데이터정의어(DDL) - Table
객체(테이블, 뷰, 인덱스 등)를 생성, 수정, 삭제하는 명령
테이블 관련 DDL 종류 : create table, alter table, drop table, truncate table(테이블 절단)
테이블 생성(create table)
SQL>
create table 테이블명
(컬럼명1, 데이터타입(컬럼사이즈),
컬럼명2, 데이터타입(컬럼사이즈) [default 기본값],
컬럼명3, 데이터타입(컬럼사이즈) [제약조건]);
()안에 테이블을 구성할 컬럼
테이블명, 컬럼명은 한글을 사용하지 않음.
'KDT > DB' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 231222 DB - 데이터정의어 3 (0) | 2023.12.22 |
|---|---|
| 231220 DB - 데이터 정의어 2 (0) | 2023.12.20 |
| 231208 DB - 서브쿼리 2, 데이터 조작어 1 (0) | 2023.12.08 |
| 231206 DB - 그룹 함수와 그룹화 2, 서브쿼리 1 (0) | 2023.12.06 |
| 231129 DB - 단일행함수 3, 그룹 함수와 그룹화 1 (0) | 2023.11.29 |